
By Dr. Gopala Krishna Behara
Today, more than ever before, and often without noticing it, technology touches every part of our lives. The adoption of next generation technologies, automated tools, agile and Devops methodologies by an organization made the role of IT as a crucial factor for the business transformation. The ability to harness these powerful technical capabilities and use them to support the business is both challenging and rewarding. Achieving synergy between people, processes and technology is not an easy task by any measure. The CIO’s of the organization must formulate a modern IT strategy that in line with the new realities.
The IT strategy also called technology strategy. It guides in how IT helps businesses to win in their chosen business context. In first place, the business needs of IT to be successful are,
- Helps in better communication and coordination between business functions and lines of business with the IT Organization
- Scale to handle increasing demands on business growth
- Security in all its operations
- Ability to understand and anticipate organization customer needs
- Manage a large variety and velocity in customer growth
As part of engaging with various customers in defining the IT Strategy, the author viewpoint is many of the IT strategy initiatives are aspirational and unachievable goals and strategies. Organizations simply document the IT strategy artefacts and shelf them or discontinued at the middle of the implementation. Many Organizations get confused between IT Strategy and Enterprise Architecture Initiatives. In author’s opinion, the drafting of IT strategy should be consistent and actionable.
This paper focus on methodology to be adopted in defining the IT strategy in digital era and the best practices that can help organizations to be more successful.
Drivers for IT Strategy
IT Strategy is a plan to create an Information Technology capability for maximizing the business value for the organization. IT capability is the Organization ability to meet business needs and improve business processes using IT based systems. The Objective of IT strategy is to spend least amount of resources and generates better ROI. It helps in setting the direction for an IT function in an organization.
A successful IT strategy helps the organizations to reduce the operational bottlenecks, realize TCO and derive value from technology.
The following are the drivers for the IT strategy definition in the Digital Era,

Fig 1: Drivers for IT Strategy in Digital Era
Technology Change: Change in technology is constant. Adoption of new technologies in near real time is mandatory for the Organization to sustain in the market.
Social Media: Social Media is the quick way of sharing information by the end users. It is very critical in developing a solution for the business problem. This feature needs to be integrated with the IT Strategy definition.
Mobility: This helps the Online/Mobility services of business processes to enable easy access & provisioning of process for customers, service providers and business users.
Open Source Adoption: Evaluate the usage of Open Source technologies for both software and hardware to cut the dollar spending by an organization.
Cloud: Almost all the Organizations are moving from On-premises to Cloud for better TCO. Adopting different models like SaaS, PaaS & IaaS across the IT portfolio.
Automation: Robotic Process Automation for the automation of the process need to be verified. Explore the usage of technologies like Machine Learning, Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality to be the part of IT portfolio of an organization.
Security: It plays a crucial role in securing the Organization assets and business. Need to decide which to guard against and how much to spend to stay safe. The factors like Performance, Quality, Reliability and Scalability are most fundamental aspects to run the organization smoothly.
Development Methods & Tools: Adoption of Agile and DevOps helps the Organizations in establishing rapid development model and support the business change.
All the above drivers demand for the IT strategy for an organization rather than an Ivory Tower and traditional way of Strategy definition approach.
IT Strategy Vs Business Strategy
IT Strategy supports and drives the Business Strategy. IT Strategy helps in achieving better business and IT alignment. The output of IT Strategy is Enterprise Architecture.
Chief Information Officer (CIO), the leader of IT Organization is responsible for formulating and implementing the IT Strategy. Some organizations have a Chief Technology Officer (CTO) role with or without the CIO role. CIO/CTO’s work closely with business functions/lines of business, Chief Operating Officer (COO), Chief Marketing Officer (CMO), and Chief Financial Officer (CFO) to execute IT Strategy. The CIO and CTO’s work closely to create an IT Strategy for the Organization.
IT strategy is developed based on the key parameters like, where the Organization today, where it wants to be in next 3 to 5 years. The critical elements of the IT Strategy definition like Business drivers, IT drivers, Business Imperatives, business capability driven by IT capability are considered.
The role of IT Strategy across Organization and its relationship with Business Strategy and Enterprise Architecture is depicted below,
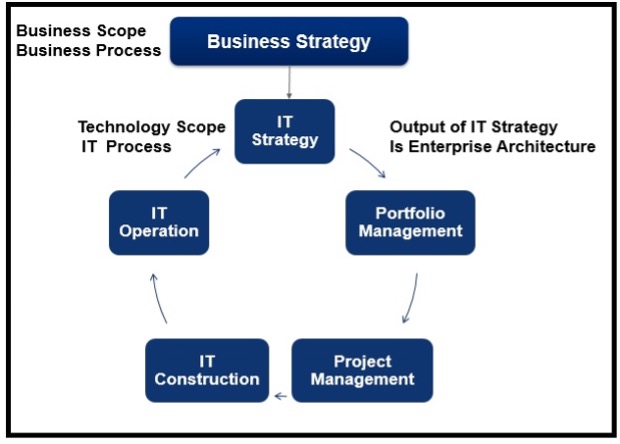
Fig 2: Role of IT Strategy across Organization
In general, the IT strategy combines an approach (“why” and “how”) with a plan (“what”, “who”, “where”, and “when”) to provide a Roadmap for an organization or IT division.
IT Strategy Methodology
IT Strategy definition and implementation covers the key aspects of technology management, planning, governance, service management, risk management, cost management, human resource management, hardware and software management, and vendor management.
Broadly, IT Strategy has 5 phases covering Discovery, Assess, Current IT, Target IT and Roadmap.
Idea of IT Strategy is to keep the annual and multiyear plan usual, insert the regular frequent check-ins along the way. Revisit IT Strategy for every quarterly or every 6 months to ensure that optimal business value created. The Strategy team discuss technology changes and industry trends and adjust the roadmap accordingly.
Below are the high-level phases that we adopted for the definition of IT Strategy for an Organization.
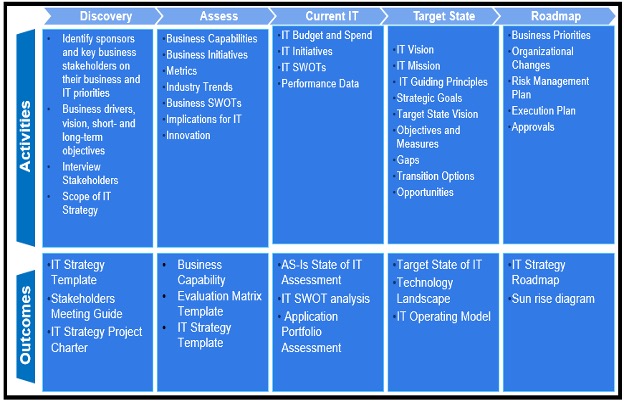
Fig 3: IT Strategy Methodology
- Discovery: Understand the organization business strategy and objectives. Identify the key stakeholders, conduct the interviews, and determine the mandate for the definition of IT Strategy. Spend significant amount of time with key stakeholders to understand the requirements of the IT strategy. Address the concerns of stakeholders who have the most power and who affected more in the IT strategy development effort. As part of this phase, discuss stakeholder concerns, information needs, and desired uses of IT strategy. IT Strategy project development charter shall be finalized during this phase.
- Assessment: Identify key business drivers and review Business capabilities and business initiatives. Drivers are events, conditions, and decisions outside the realm of IT that affect the IT strategy. They can exist within organization or in the external environment. A business capability is an abstraction that helps describe what the organization does to achieve its vision, mission, and goals. Business capabilities are the building blocks of the organization. Perform Business SWOT analysis helps to identify the trends that must leverage and risks that must be mitigate. Listing of IT Metrics to measure the performance of business strategy done during this phase.
- Current State IT: Assess current “As Is” case covering core business functions, business operations, processes and services. Also, business applications / solutions and technical infrastructure architecture landscape. Examination of the current operations line, services, products and infrastructure are done. Assess IT organization structure and Human Resources to re-align to organization cater and growth. Assess automation levels of business process and services for each department with classification schema for the services provided by each entity along with business benefits, revenue and benefits to customer and employees. Understand current disaster recovery and business continuity covering enterprise level along with IT practices related to Disaster Recovery and Business Impact Analysis. Leverage the analysis tool to examine current implemented solutions cross organization – Like SWOT or any other tools.
- Target State IT: In this phase, understand the organization future growth plan and business strategy. Revisit IT vision, mission and guiding principles of an organization, if already defined. Identify the IT improvement opportunities with alignment toward organization business strategy. Define demand projections covering different techniques for effective and efficient business operations. It enhances the development of target IT architecture while covering the best opportunities and utilization of following key focus areas,
- Business process automation
- Compliance and assurance
- Social media
- Digital Transformation
- Intelligence Solutions and Data Management
- Cloud and Mobility
- IT Security
- Innovative Trends, internal and external benchmarks
- External trends and influences either globally or locally
- Demand projections covering different techniques for effective and efficient business operations
As part of Target state IT, revisit IT Organization, roles and responsibilities in line with organization practices and framework. Best practices and latest technology and market trends in technology horizon with specific regard to domain.
- Roadmap: In this phase, develop the IT strategy roadmap in executive level as well as detail level. The roadmap shall focus on the defined key focus areas and IT strategic pillars. It also addresses the implementation plan of the IT strategy spanning in short term, midterm and long term with prioritization of initiatives, objective description, cost along with key business benefits and success factors.
Best Practices for developing IT Strategy
A clear IT Strategy is the most important activity of CIO/CTO of an Organization to achieve the business goal and benefits to the business. IT Strategy is a continuous process; it is not a one-time activity. IT strategy needs to adapt to changing business needs and customer demands. Visit the Strategic planning and its implementation status frequently. Also, the IT leaders continuously adapt innovate strategies to leverage new technologies, address emerging risks, and meet Organization goals and objectives.\
The following are the best practices for developing IT Strategy,
- Involve business stakeholders as part of the definition of IT Strategy
- Always craft the IT Strategy plan that is actionable and conduct the check regularly
- Use common language and teams that are domain specific and used across the Organization
- A successful IT strategy is always defined at the CIO/CTO level
- Every strategy pillar must support organizational goals. Develop a small, select set of goals that drive Organization towards vision
- The implementation plan should reflect current realities and constraints
- Conduct measurement checks to ensure progress toward goals
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Santosh Shinde of BTIS, Enterprise Architecture division of HCL Technologies Ltd for giving the required time and support in many ways in bringing this article as part of Architecture Practice efforts. The author would also like to thank Myra Chaganty, Austin, USA for all the necessary support to develop this paper.
Author
Dr. Gopala Krishna Behara is an Enterprise Architect in the BTIS Enterprise Architecture division of HCL Technologies Ltd. He has a total of 27 years of IT experience. Reached at gopalakrishna.behara@gmail.com.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this article/presentation are that of authors and HCL does not subscribe to the substance, veracity or truthfulness of the said opinion.
